Reverse Transcriptase Template Switching

In the absence of rnase h switching still occurred but the efficiency was lowered.
Reverse transcriptase template switching. The basic reaction with rna templates and normal reverse transcriptase yielded as much as 83 template switching. During reverse transcription of a retroviral genome reverse transcriptase rt enzyme must undergo two template switching events which occur at the ends of the template to complete dna synthesis rt undergoes frequent additional switches of templates leading to a great variability in retroviral populations these template switching ts events are generated in a homology dependent manner. Thus we considered an in vitro artifact during rt pcr as a possible explanation for this observation. In contrast to reverse transcriptase taq dna polymerase or c.
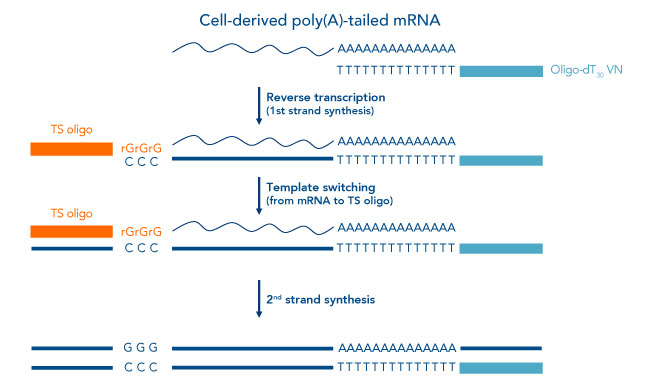
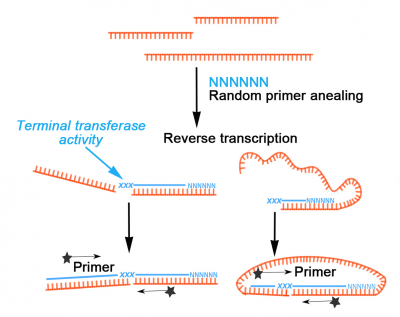
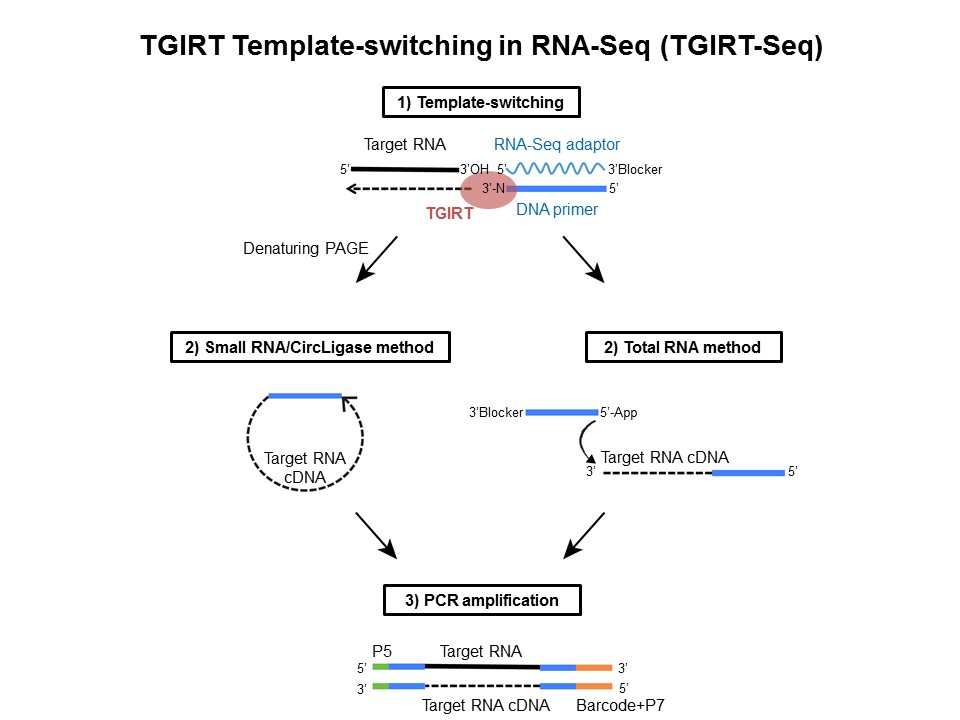
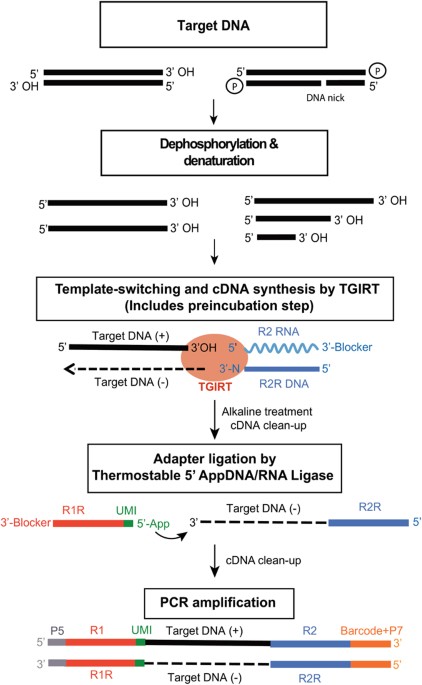
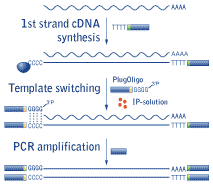
The reverse transcriptases rts encoded by mobile group ii introns and other non ltr retroelements differ from retroviral rts in being able to template switch efficiently from the 5 end of one template to the 3 end of another with little or no complementarity between the donor and acceptor templates. These non templated nucleotides can anneal to a template switching oligo tso with a known sequence prompting the reverse transcriptase to switch template from rna to the tso. Here we describe a fast simple method for constructing full length cdna libraries using smart technology. In order to understand such switching we used in vitro reactions with purified nucleic acids and enzymes.
The ability of reverse transcriptase to make template switches during dna synthesis is implicit in models of retrovirus genome replication as well as in recombination and oncogene transduction. However use of a template switching chimeric dnarna oligo and mmlv reverse transcriptase can improve on this. Based on several studies using high frequency deletion of homologous repeats as a model system we proposed a dynamic copy choice model for retroviral recombination which postulated that there is a steady state between the rates of dna synthesis and rna. Template switching polymerase chain reaction ts pcr is a method of reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction pcr amplification that relies on a natural pcr primer sequence at the polyadenylation site also known as the polya tail and adds a second primer through the activity of murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase.
Conventional cdna construction strategies usually result in an underrepresentation of the 5 ends of cdna. This novel procedure uses the template switching activity of moloney murine leukemia virus mmlv reverse transcriptase to synthesize and anchor first strand cdna in one step.